通常在开发项目的时候,会先生成数据字段的Excel表,然后在MySQL中创建对应的数据表,字段少的时候还不是很麻烦,但是遇到字段特别多的表时,手写SQL效率会非常低下,像Navicat等图形化工具支持从Excle导入,但是操作繁琐而且容易出错,这时候就需要一些工具来帮我们生成数据表了。
需求
从一个数据库设计的Excel表生成MySQL数据表,假设现在有一个设计好的Excel表结构,像下面这样,需要用它来生成数据表。
| 名称 |
字段名 |
类型 |
长度 |
| ID |
id |
int |
11 |
| 姓名 |
name |
varchar |
10 |
| 年龄 |
age |
int |
3 |
| 生日 |
birthday |
date |
实现
这里实现的时候使用到了Apache POI这个库,POI编写了非常多实用的API,它可以使用Java读取、创建和修改MS Excel文件,官方文档:POI
实现的思路是,利用POI,可以非常方便的解析上面的Excel表,读取里面的字段值,注释,类型和长度等,再拼接成SQL,利用JDBC执行,就可以生成数据表结构了。
代码如下(JDK8):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| package cn.glieen;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellType;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Excel2MySQL {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
String fileName = "user.xlsx";
Sheet sheet = loadExcel(fileName);
String sql = createSQL(sheet, fileName);
System.out.println(sql);
executeSQL(sql);
}
public static Sheet loadExcel(String fileName) throws IOException {
InputStream excelResource = Excel2MySQL.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(fileName);
Objects.requireNonNull(excelResource);
XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(excelResource);
return wb.getSheetAt(0);
}
public static String createSQL(Sheet sheet, String fileName) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("CREATE TABLE ");
String tableName = fileName.substring(0, fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
sb.append("`").append(tableName).append("`(");
int rowNum = sheet.getLastRowNum();
for (int i = 1; i < sheet.getLastRowNum() + 1; i++) {
Row row = sheet.getRow(i);
sb.append(parseField(row));
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.lastIndexOf(","));
sb.append(");");
return sb.toString();
}
public static String parseField(Row row) {
String comment = getCellValue(row.getCell(0));
String name = getCellValue(row.getCell(1));
String type = getCellValue(row.getCell(2));
String length = getCellValue(row.getCell(3));
if ("".equals(length)) {
length = "";
} else {
length = "(" + length + ")";
}
return "\n`" + name + "` " + type + length + " COMMENT '" + comment + "',";
}
public static String getCellValue(Cell cell) {
cell.setCellType(CellType.STRING);
return cell.getStringCellValue();
}
public static void executeSQL(String sql) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
try (Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
}
connection.close();
}
}
|
运行结果:
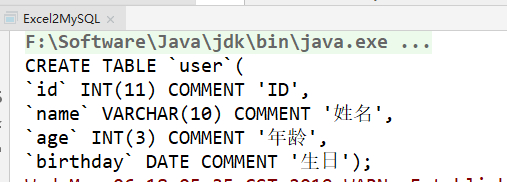
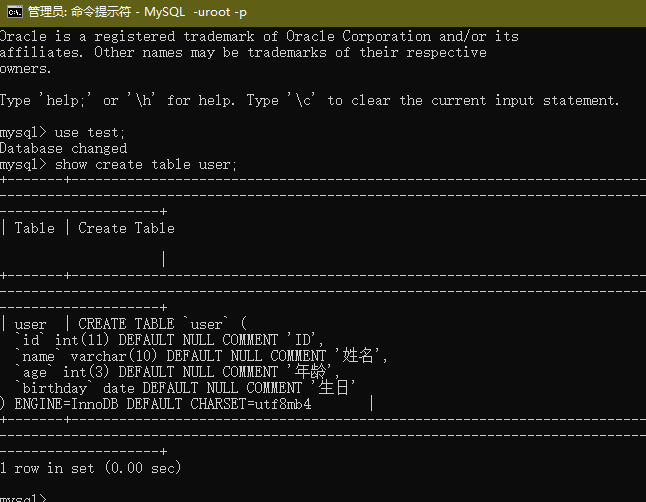
SQL语句成功打印,数据表成功创建。
扩展
上面只是一个简单的Demo,当需要更多的功能,比如,自增长,主键和索引等内容时,可以对代码进行更丰富的扩充和完善。这只是简单使用了POI的一小部分,更多的处理接口还待发现。

